

India’s agriculture feeds over 1.4 billion people and sustains nearly 60% of the nation’s workforce. With 156 million hectares of farmland, the country stands among the world’s largest agricultural economies. But this strength comes with growing pressure — energy demand, water scarcity, and climate unpredictability are testing India’s food systems.
As the nation races toward its 500 GW renewable energy target by 2030, a revolutionary model called agrivoltaics is showing how solar power and farming can thrive together.
What is Agrivoltaics?
Agrivoltaics, or agri-solar, is the practice of growing crops beneath or between elevated solar panels. Instead of competing for land, sunlight is shared — part goes to photosynthesis, part to power generation.
In India’s field trials, this model has shown 60–70% higher total productivity compared to conventional single-use systems. The reason? Solar panels reduce excessive heat stress and evaporation, while the crops help keep the panels cooler — a win-win for both yields and energy efficiency
It’s a sustainable innovation designed to tackle land scarcity, rural income challenges, and the energy transition — all at once.
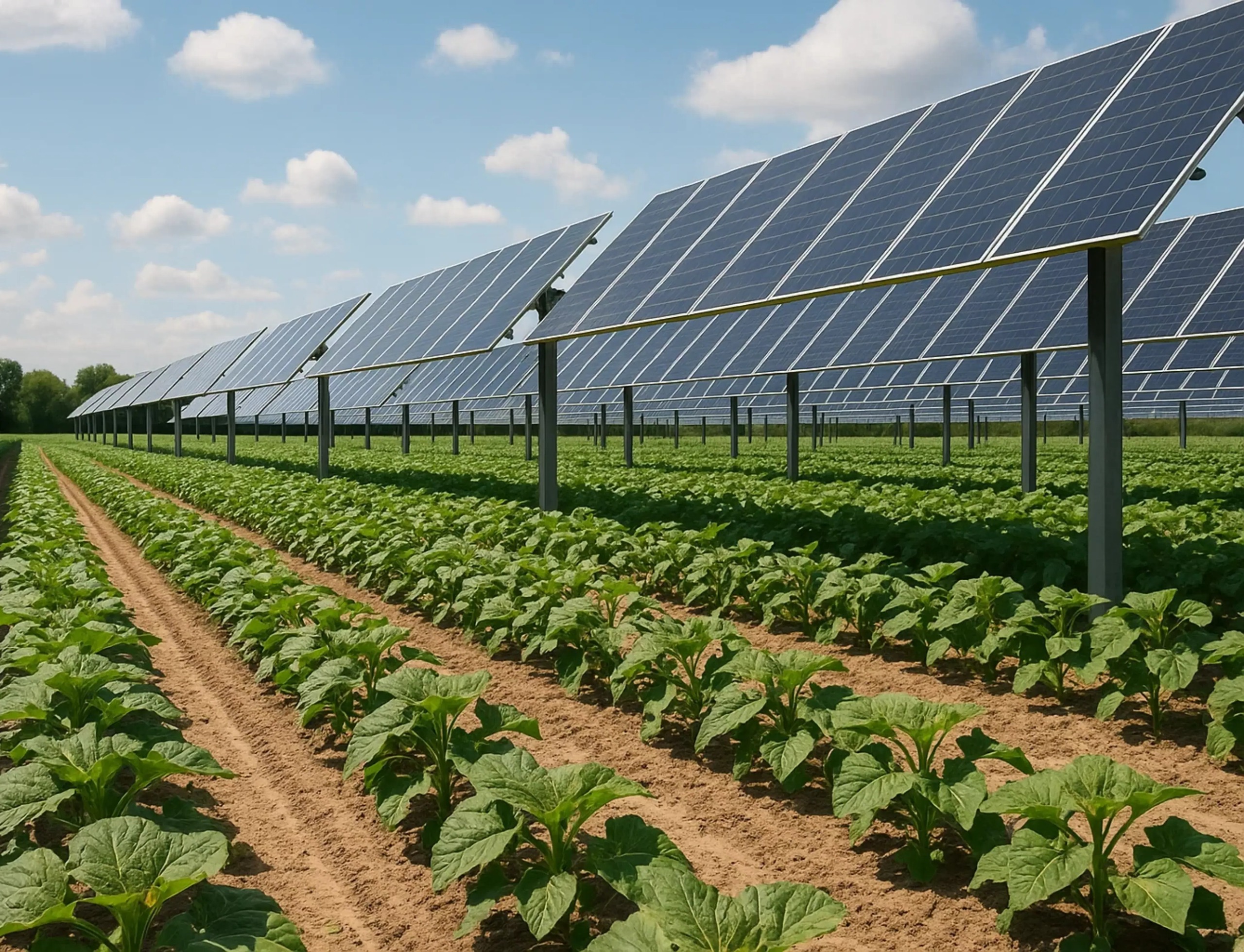
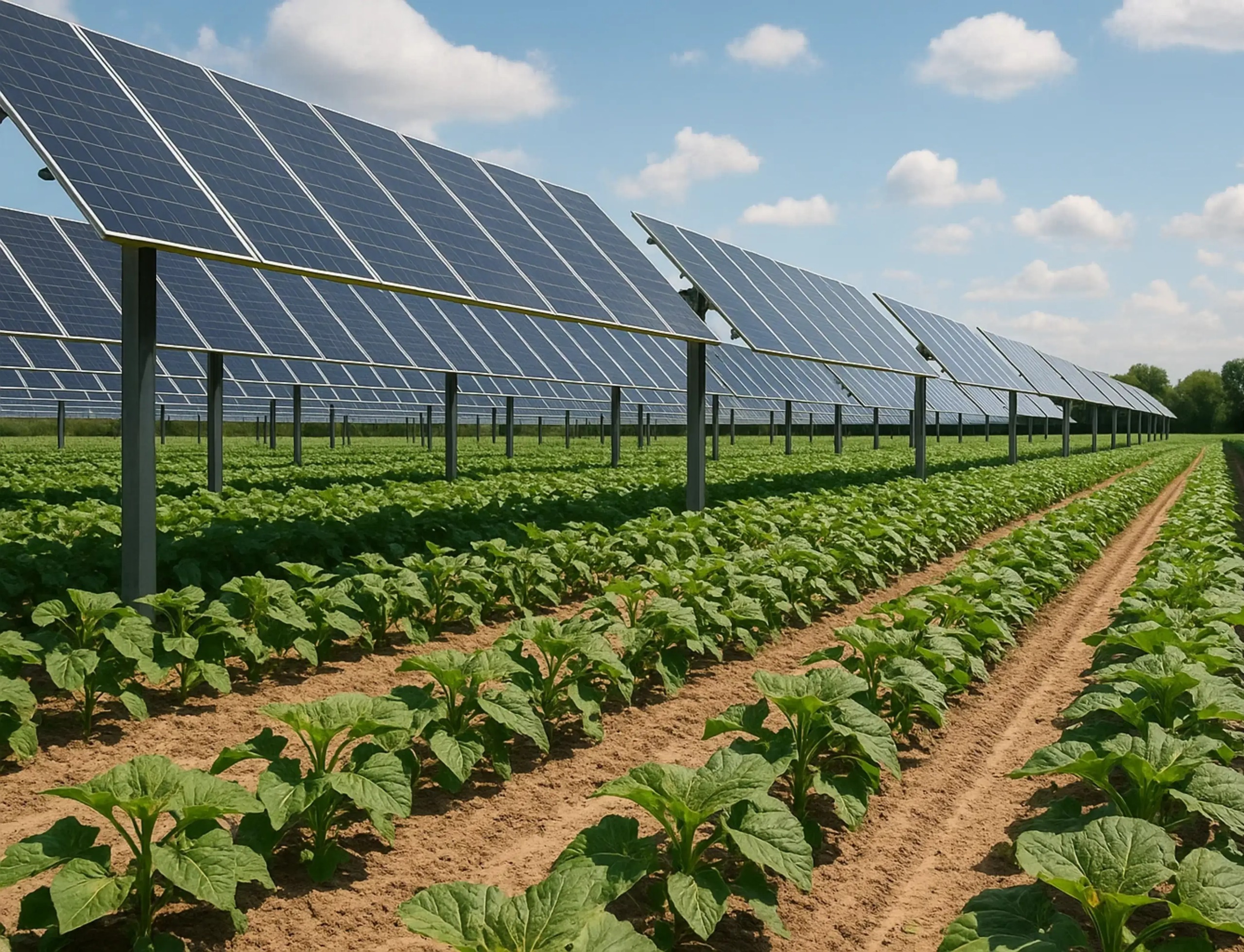


India’s Policy Push for Agrivoltaics
India has the world’s third-largest renewable energy capacity, is actively promoting agrivoltaics in India.
Over 25 pilot projects and hundreds of demonstration sites are operational or planned, proving that solar and agriculture can coexist sustainably.
Why It’s a Worthwhile Investment
- Lifespan: Over 25+ years, these projects offer substantial savings on electricity bills.
- ROI: The long-term return on investment ensures financial viability for industries and businesses.
1. PM-KUSUM Scheme (MNRE)
Launched in 2019 and expanded in 2024, the Pradhan Mantri Kisan Urja Suraksha evam Utthan Mahabhiyan (PM-KUSUM) scheme encourages farmers to adopt solar technology. Key highlights:
- Subsidies cover up to 60% of capital costs, with additional support through loans and farmer equity.
- Component A: Large-scale solar plants (up to 2 MW) on uncultivable land.
- Components B & C: Solar-powered irrigation pumps for farms and communities.
PM-KUSUM is instrumental in promoting agrivoltaic systems, providing a structured framework for dual-use of land.
2. State-Level Push
Several states have launched targeted programs to support agrivoltaics in India:
- Maharashtra: The Mukhyamantri Saur Krushi Vahini Yojana (MSKVY) aims to solarize agricultural feeders, targeting 13.65 GW by 2026. Farmers benefit from fixed feed-in tariffs (₹3.10/kWh) and income diversification.
- Gujarat: Suryashakti Kisan Yojana (SKY) provides up to 60% financial support for PV systems and guarantees tariffs for grid-supplied power (₹7/kWh for 7 years).
- Delhi: The Mukhyamantri Kisan Aay Badhotri Solar Yojana enables farmers to lease their land for solar projects, earning a stable monthly income of ₹8,333 per acre.
- Odisha: Farmers receive ₹20,000 per acre/year for participating in solar installations, supplementing rural income.
3. Strategic Collaborations & Research
- India Agrivoltaics Alliance (IAA): A collaborative platform of government agencies, research institutions, and farmer groups that standardizes APV systems and promotes best practices.
- International Partnerships: Indo-German R&D collaborations and Centre of Excellence help develop locally adapted agrivoltaics solutions suitable for India’s diverse agro-climatic zones.
Evidence from the Field
Agrivoltaic pilots across India are showing measurable success:
- Crops: Wheat, tomato, turmeric, pulses, spinach, and coriander thrive under shade panels.
- Water Savings: Soil evaporation reduced by up to 30%, lowering irrigation demand.
- Yield Trends: Shade-tolerant crops match or outperform open-field yields.
Examples:
- Nagpur’s floating solar irrigation model
- Delhi’s KVK pilot under ICAR supervision, done by Ornate Solar
- Agra-Dayalbagh and Amity University’s dual-income projects
Some sun-loving crops may underperform if panel density is excessive, highlighting the need for optimized spacing and smart solar tracking.
Economics and Farmer Impact
Agrivoltaic systems require higher upfront investment than conventional setups, but payback is promising.
- Capital recovery: 4–7 years (average, per MNRE & state pilot data)
- Post-payback ROI: Stable, long-term dual income through energy sales + crop yield
- Subsidy mix: 60% capital subsidy + 30% institutional loan under PM-KUSUM
- Feed-in tariffs: ₹3.10–₹7 per kWh depending on state and project scale
Upcoming policies under the National Agrivoltaics Mission (draft stage) aim to:
- Target 10–15% of India’s agricultural land for agrivoltaics adoption by 2035
- Provide Viability Gap Funding (VGF) and training programs for smallholders
Sustainability and Social Impact
Beyond clean power and income, agrivoltaics strengthens rural sustainability:
- Prevents agricultural land diversion for large solar parks
- Creates local employment for installation and maintenance
- Empowers FPOs and women-led collectives to co-own renewable assets
- Enhances climate resilience by shading crops and retaining soil moisture
The result? Energy self-sufficiency for rural India — powered by the very land that feeds the nation.
Common FAQs
Conclusion
Agrivoltaics is more than a farming innovation — it’s India’s blueprint for sustainable land use.
By merging food production with solar generation, India can secure its energy future, protect farmlands, and uplift rural incomes.
The sun that once nourished crops now powers prosperity too.
About Ornate Solar
Ornate Solar is a leading solar company with 10 years of experience in the industry and the mission to reimagine the way solar is installed worldwide.
By not only partnering with the best-in-class solar brands but also developing our high-quality solutions (panels, inverters, accessories, InRoof), we develop and deliver solutions that are modern, reliable, and effective.
Ornate Solar is also a trusted BESS manufacturer in India. We have developed UnityESS, an advanced energy storage solution to provide reliable power and energy independence.
If you are looking for high-quality solar solutions, reach out to us at 1800 2026 252 to discuss your options










Leave A Comment