

Scientists have been making groundbreaking discoveries in solar power for two centuries now. Join us as we uncover the evolution of solar energy, from its early beginnings to the modern innovations that shape our world today.
The Discovery of the Photovoltaic Effect:
In 1839, physicist Edmond Becquerel discovered the photovoltaic effect, which generates electric current when certain materials are exposed to light. This pivotal discovery laid the foundation for solar energy conversion.
Augustin Mouchot’s Solar-Powered Engines:
Inspired by Becquerel’s work, mathematician Augustin Mouchot patented solar-powered engines in the 1860s, showcasing solar energy as a viable alternative.

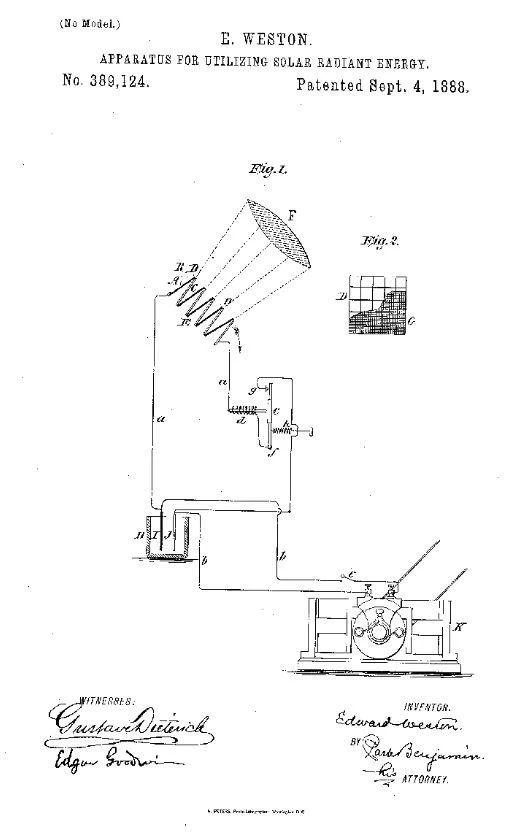
Edward Weston’s Solar Cell Patents:
In 1888, inventor Edward Weston obtained patents for solar cells, proposing to transform radiant energy into electrical or mechanical energy. He introduced thermopiles, devices that convert thermal energy into electricity, to capture the sun’s power.
Aleksandr Stoletov and the Photoelectric Effect:
Also in 1888, Russian scientist Aleksandr Stoletov developed the first solar cell based on the photoelectric effect, paving the way for modern solar cell technology.
Melvin Severy’s Solar Cell Patents:
In 1894, American inventor Melvin Severy received patents for solar cells that harnessed solar heat to generate electricity. His designs incorporated mechanisms to track the sun’s movements for optimal energy capture.
Harry Reagan and Thermal Batteries:
During the late 1890s, inventor Harry Reagan patented thermal batteries, which stored and released thermal energy. While not directly storing electricity, these batteries played a crucial role in utilizing thermal energy to generate electricity through conventional turbines. Bell Laboratories and Silicon Solar Cells:
Fast forward to the 1950s when Bell Laboratories made a groundbreaking breakthrough in solar cell technology. Inventors Daryl Chapin, Calvin Fuller, and Gerald Pearson pioneered the development of efficient silicon solar cells. These cells converted sunlight into electricity with an impressive 6% efficiency. Although cost-prohibitive at the time, they marked a significant milestone as the first practical devices for converting solar energy into usable electricity. Bell’s innovative work paved the way for harnessing the power of sunlight, but there was one challenge – cost. Producing silicon solar cells was quite expensive, making them inaccessible for most people. Even creating a solar panel by combining multiple cells made them more costly.
First Solar Building
In 1973, the University of Delaware created one of the first solar buildings called “Solar One.” This construction relied on a combination of solar thermal and solar photovoltaic power. And guess what? They didn’t use traditional solar panels. Instead, they integrated solar technology right into the rooftop of the building.
Solar Energy’s Rise and Government Support:
The energy crisis of the 1970s sparked a renewed interest in solar energy as an alternative source. Governments began recognizing the importance of solar research and development. In 1974, the United States passed the Solar Energy Research, Development and Demonstration Act, showcasing a commitment to advancing solar technology. Grants and tax incentives further accelerated the growth of solar energy, making it more accessible for widespread adoption.
Efficiency Improvements and Cost Reduction:
Over the years, scientists and engineers have worked tirelessly to improve the efficiency and affordability of solar panels. Through the refinement of manufacturing processes and the use of new materials, solar cells have become more efficient, capturing a greater percentage of sunlight and producing more electricity per square meter. As a result, the cost of solar panels has significantly decreased, making them increasingly accessible to a wider audience.
Multi-Junction Solar Cells
During the 1990s, researchers began focusing on enhancing the efficiency of photovoltaic (PV) cells. This led to the development of multi-junction solar cells, which achieved efficiencies above 30% by the early 2000s. These high-efficiency solar cells opened new possibilities for more cost-effective and productive solar energy systems.
Thin-Film Technologies
One significant development during this time was the National Renewable Energy Laboratory’s (NREL) work on thin-film solar technologies. Thin-film solar cells are lightweight, flexible, and offer a potential low-cost alternative to traditional silicon-based solar cells. NREL researchers explored materials like amorphous silicon, cadmium telluride, and copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) to create these innovative solar cells.
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP)
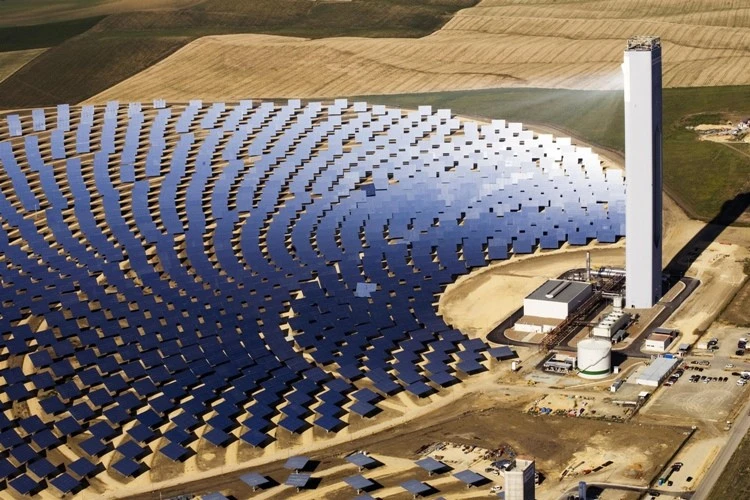

Advancements in concentrated solar power (CSP) systems have been made during the 2000s. CSP technology utilizes mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight onto a receiver for electricity generation. Research during this period aimed to improve the efficiency and scalability of CSP systems, making them more viable for large-scale solar energy generation.
Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV)
Another exciting development during the 2000s was the emergence of building integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) and solar thermal systems. BIPV systems integrate solar cells into building components such as windows, roofs, and facades. This integration allows buildings to generate electricity while also serving as functional elements. Researchers focused on maximizing energy generation and integration by exploring innovative designs and materials.
Energy Storage and Grid Integration
The 2010s marked a shift towards addressing the intermittency of solar energy and enhancing its reliability through energy storage and grid integration. Advanced battery technologies became a focal point for researchers to efficiently store and utilize solar energy. Lithium-ion batteries gained popularity due to their high energy density and long cycle life.
Grid integration was another key area of focus. Smart grid technologies enabled the seamless integration of solar energy into existing power grids. Researchers investigated optimal control strategies, grid management systems, and demand response mechanisms to ensure stable and reliable grid operation.
Perovskite Solar Cells
One of the most promising technologies in solar panel development is perovskite solar cells. These solar cells utilize a crystalline material called perovskite, which has the potential to replace silicon in solar panels. By simplifying production methods and reducing costs, perovskite solar cells aim to enhance both the affordability and efficiency of solar energy.
In 2018, the Oxford Photovoltaics achieved a significant milestone by setting a new efficiency record of 28% for perovskite solar cells. This breakthrough highlighted the transformative potential of perovskite technology within the solar industry.
All these advancements in solar panel technology bring us closer to a future where solar energy becomes a reliable and cost-effective source of power. Scientists and researchers continue to explore new possibilities, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in harnessing solar energy. The ongoing efforts in multi-junction solar
About Ornate Solar
Ornate Solar is a leading solar company with 8+ years of experience in the industry and the mission to reimagine the way solar is installed worldwide.
From advanced solar panels, innovative inverter solutions, and high-quality accessories to the unique InRoof that turns panels into the primary roof, we develop and deliver solutions that are modern, reliable, and effective.
If you are exploring solar solutions, reach out to us at 011 43536666 to discuss your options. Ornate Solar’s dedicated technical team will handle the complete installation process for you.
















Learning about the early discoveries and experiments that laid the foundation for solar energy is truly enlightening. It’s a testament to human curiosity and ingenuity that these pioneers paved the way for the advanced solar technologies we have today.
Impressive read! The evolution of solar energy, from early discoveries to modern innovations, is crucial for Caribbean solar companies to embrace. #RenewableEnergy